H2O Wave is a Python package for creating realtime ML/AI applications for a wide variety of data science workflows and industry use cases.
Data scientists view a significant amount of data in tabular form. Running SQL queries, pivoting data in Excel or slicing a pandas dataframe are pretty much bread-and-butter tasks.
With the growing use of low-code tools, having a tabular component is an essential need. H2O Wave’s Table component has some fantastic features like native filtering, markdown cells, row triggers, pagination and even real-time searching that makes Wave applications incredibly useful, interactive & modern for users.
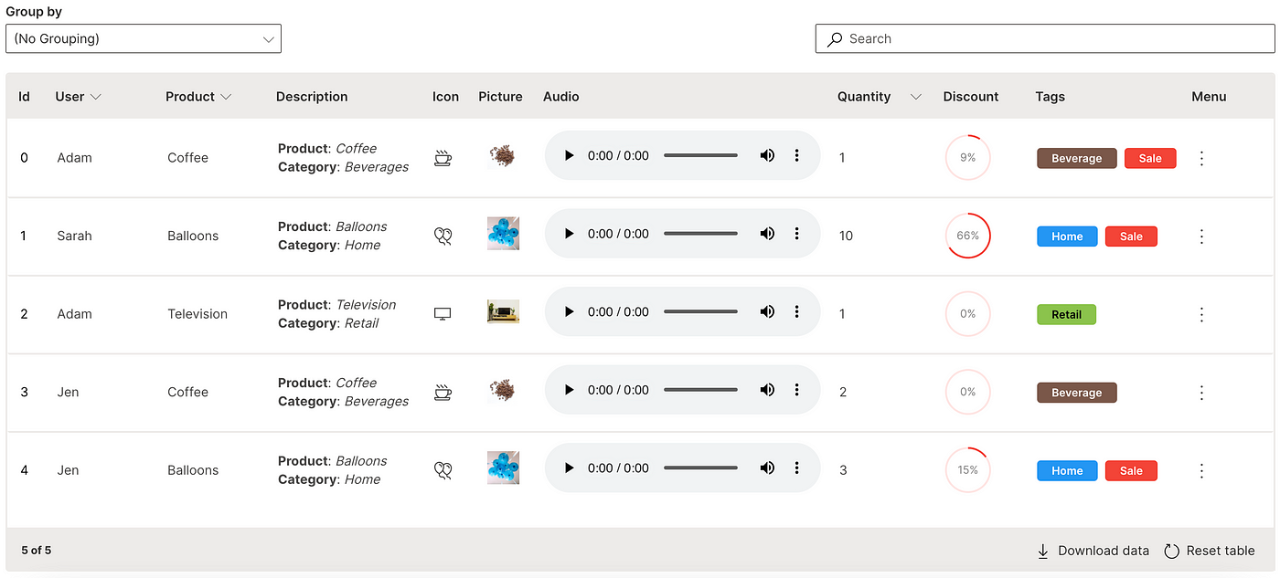

H2O Wave Table
Let’s look at some of these features along with its corresponding implementations. A simple construction of a Wave application with the table is provided below:
from h2o_wave import main, Q, app, ui
@app('/')
async def serve(q: Q):
q.page['table'] = ui.form_card(
box='1 1 -1 -1',
items=[ui.table(
...
)]
)
await q.page.save()
app.py can be run using wave run app.py after installing H2O Wave and viewed on http://localhost:10101
P.S. A full blown comprehensive application Table Showcase is also available as part of the WaveTon series.
Create
Creating a table involves defining the columns and rows of the data.
ui.table is used to define the table elements.
ui.table_column is used to define each column of the data.
ui.table_row is used to define the content of each row in the data.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
ui.table_column(name='id', label='Id'),
ui.table_column(name='user', label='User'),
ui.table_column(name='product', label='Product')
],
rows=[
ui.table_row(name='0', cells=['0', 'Adam', 'Coffee']),
ui.table_row(name='1', cells=['1', 'Sarah', 'Balloons'])
]
)
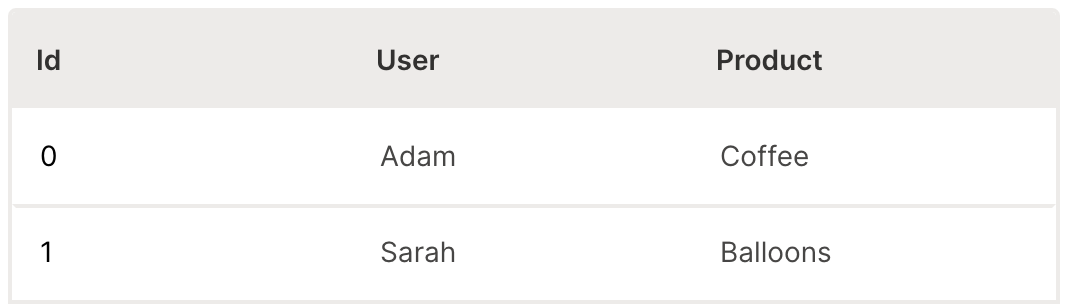

Wave Table (Create)
It’s common to have data in a csv file and the table creation can be extended to be created from an uploaded file.
An example CSV Loader application from the WaveTon series showcases how this is done.
Size
A table can be resized in multiple ways to make optimum use of space.
width is used to set the total width of the table.
height is used to set the total height of the table.
They can be set to pixel values or percentages or custom calculations.
min_width is used to set the minimum width of a column.
max_width is used to set the maximum width of a column.
The column widths can also be interactively resized directly on the table.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='user',
label='User',
sortable=True
),
ui.table_column(
name='product',
label='Product',
sortable=True
),
ui.table_column(
name='quantity',
label='Quantity'
sortable=True
)
],
resettable=True,
...
)

Wave Table (Size)
Type
The default column type of every column is string.
data_type is used to change the type of a column.
This must be set when using numeric columns to handle sorting correctly and/or timestamp columns to display neat date/time formats.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
ui.table_column(
name='id',
label='Id',
data_type='number'
),
...,
ui.table_column(
name='quantity',
label='Quantity',
data_type='number'
)
],
...
)
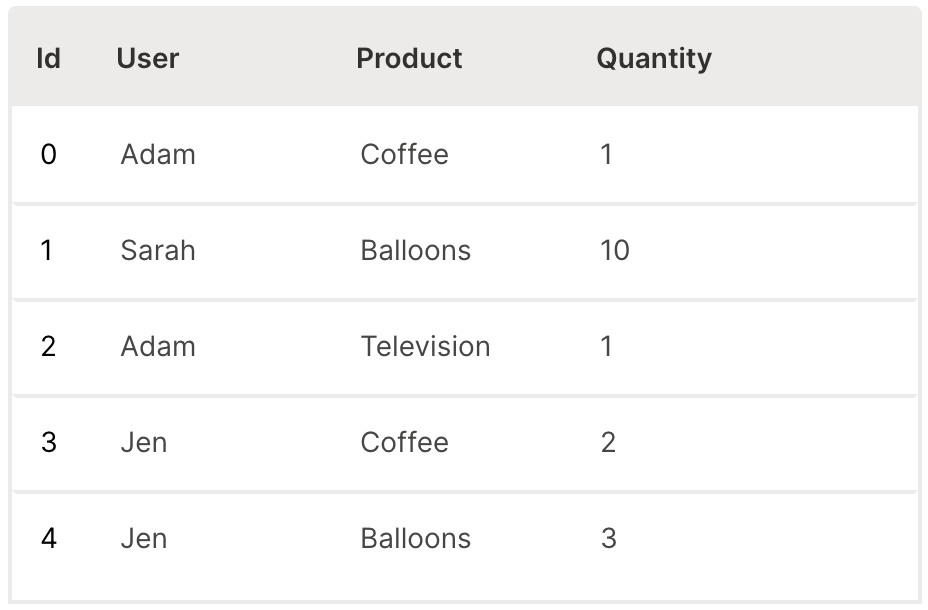

Wave Table (Type)
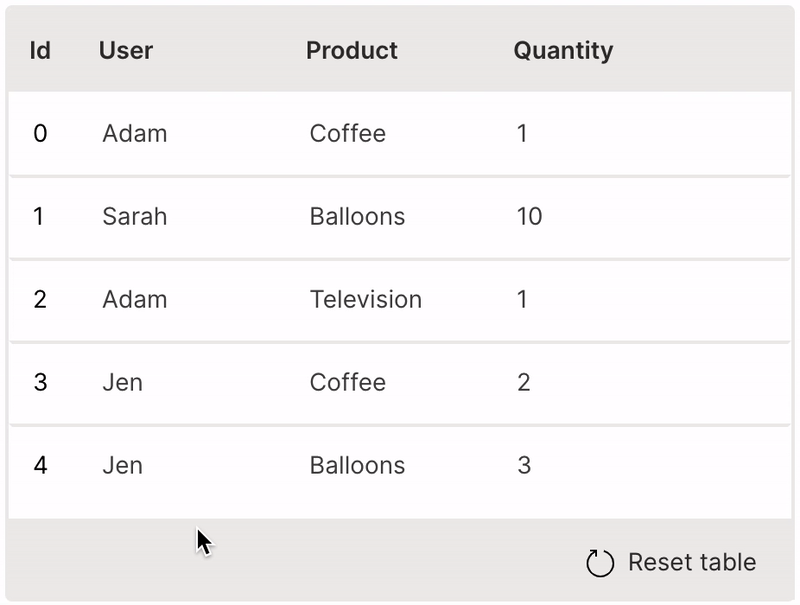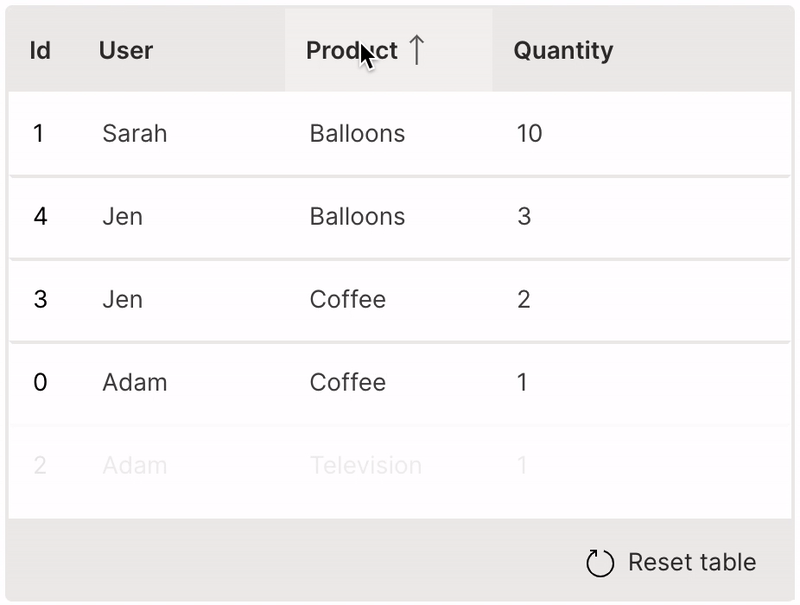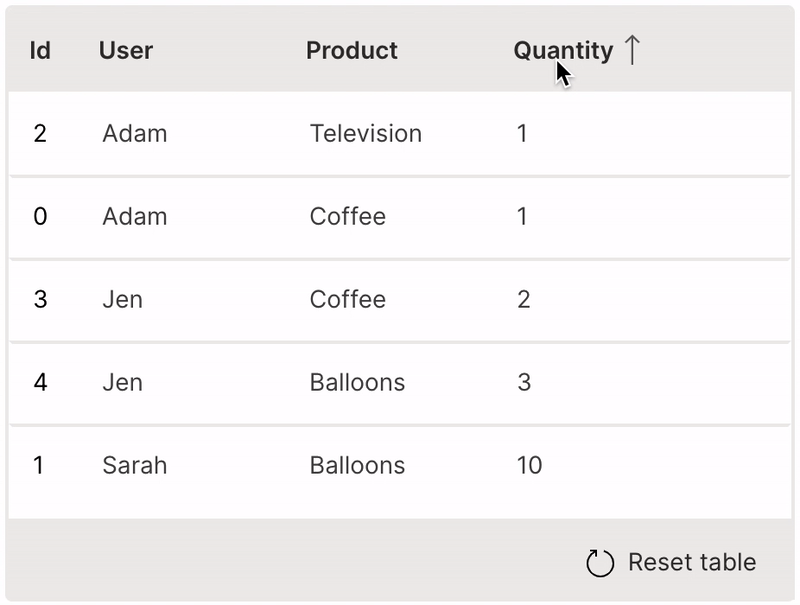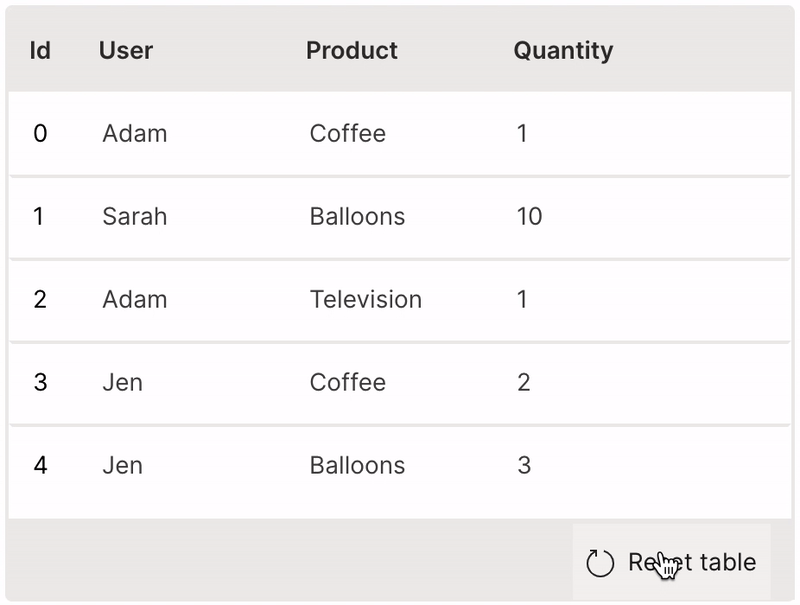
Sort
A table can be sorted by clicking its header.
sortable is used to enable sorting of a column.
It is very useful to provide the resettable option to revert the table back to its original state.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='user',
label='User',
sortable=True
),
ui.table_column(
name='product',
label='Product',
sortable=True
),
ui.table_column(
name='quantity',
label='Quantity'
sortable=True
)
],
resettable=True,
...
)

Wave Table (Sort)
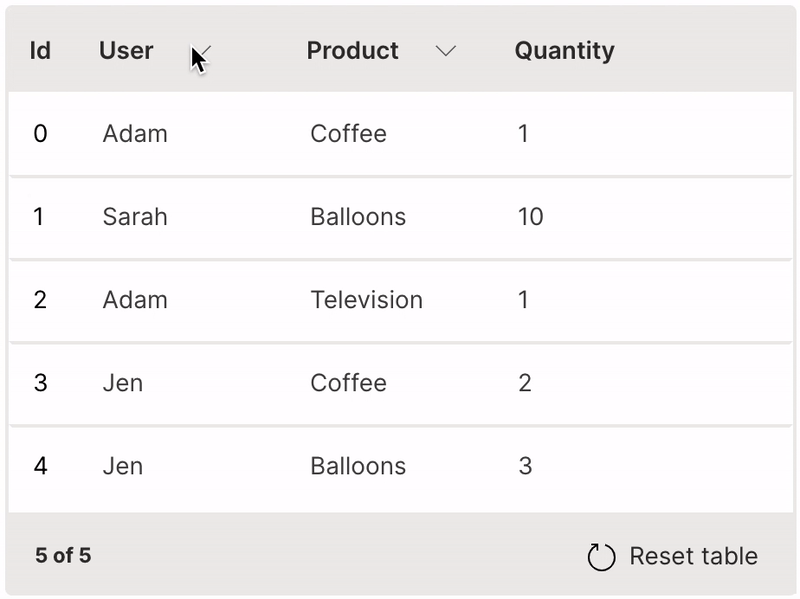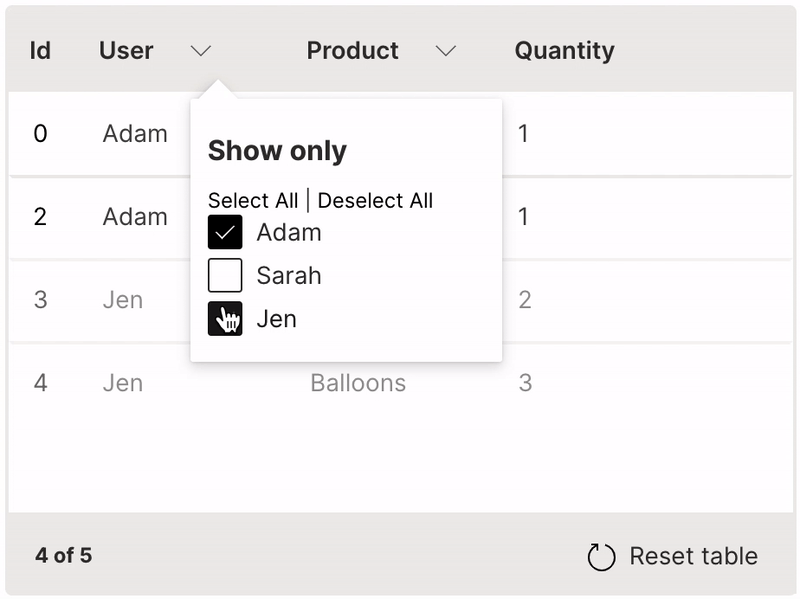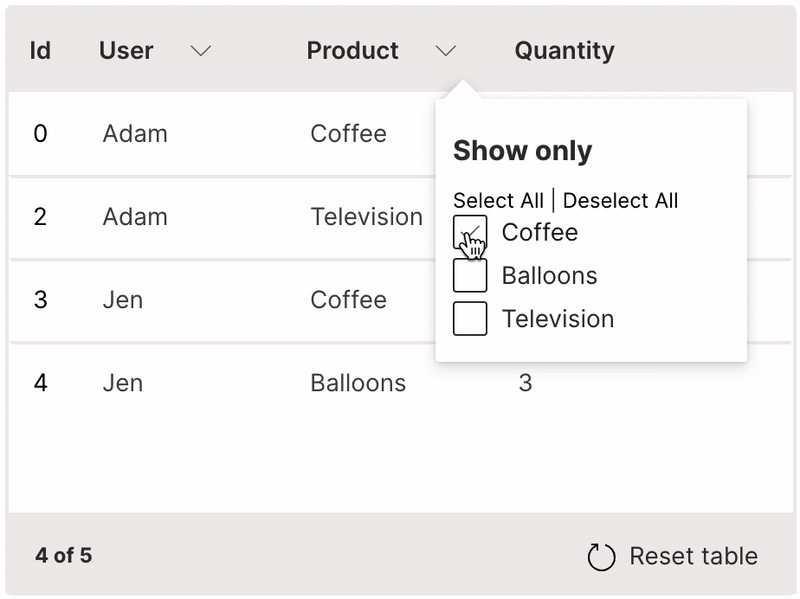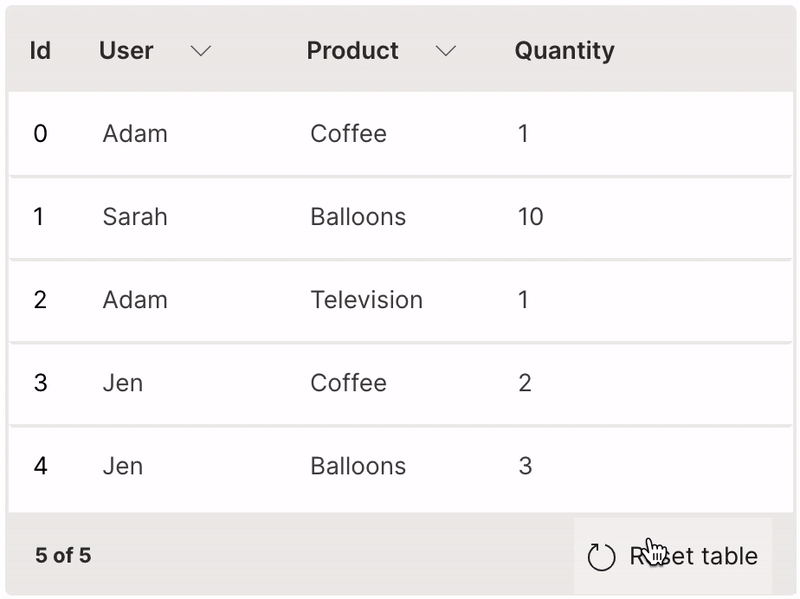
Filter
A table can be filtered by selecting values from its header.
filterable is used to enable filtering of a column.
It is very useful to provide the resettable option to revert the table back to its original state.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='user',
label='User'
filterable=True
),
ui.table_column(
name='product',
label='Product'
filterable=True
),
...
],
resettable=True,
...
)

Wave Table (Filter)
Group
A table can be viewed as groups of a particular column.
groupable is used to enable grouping of a table.
It is very useful to provide the resettable option to revert the table back to its original state.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...
],
groupable=True,
resettable=True,
...
)
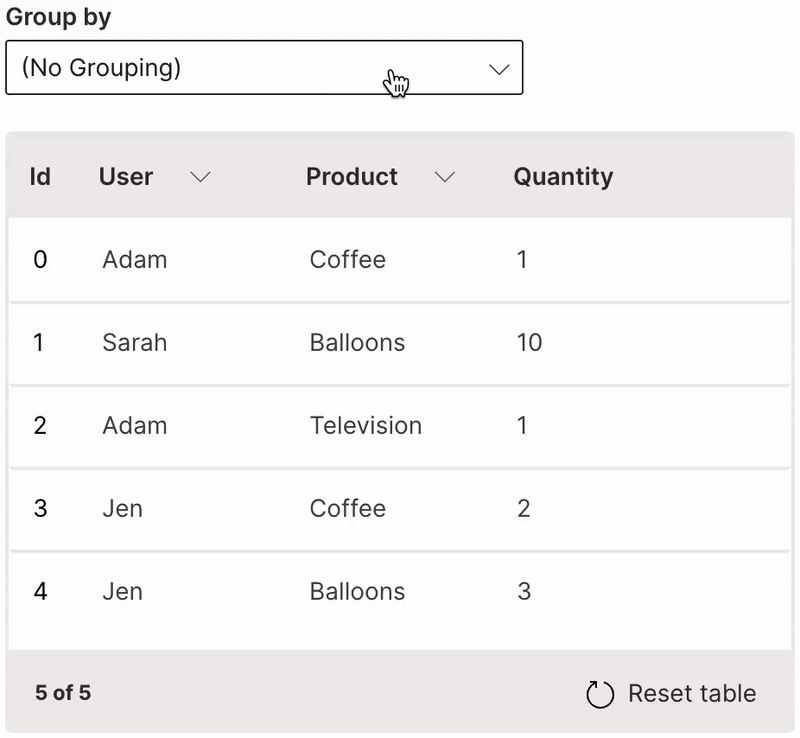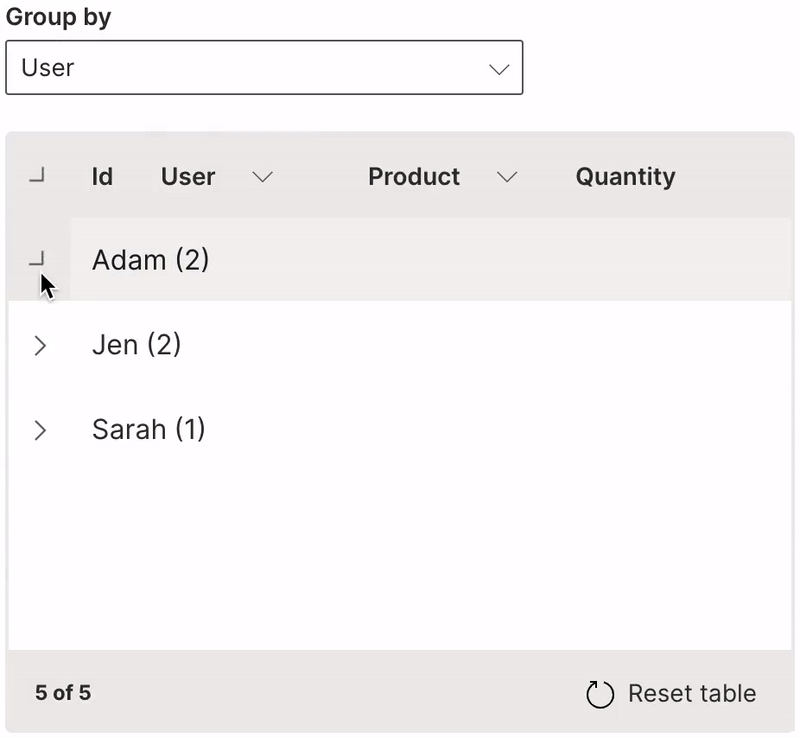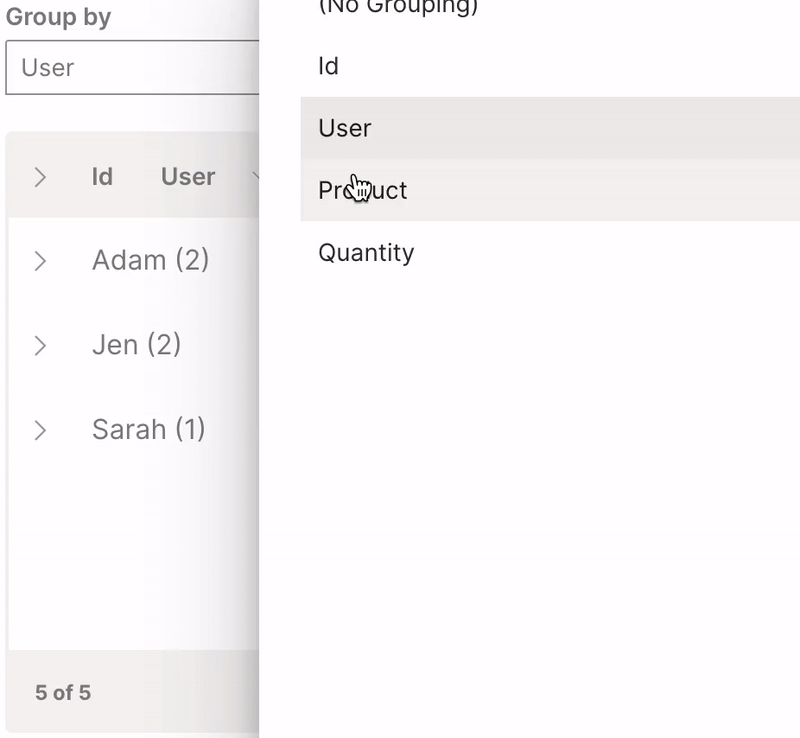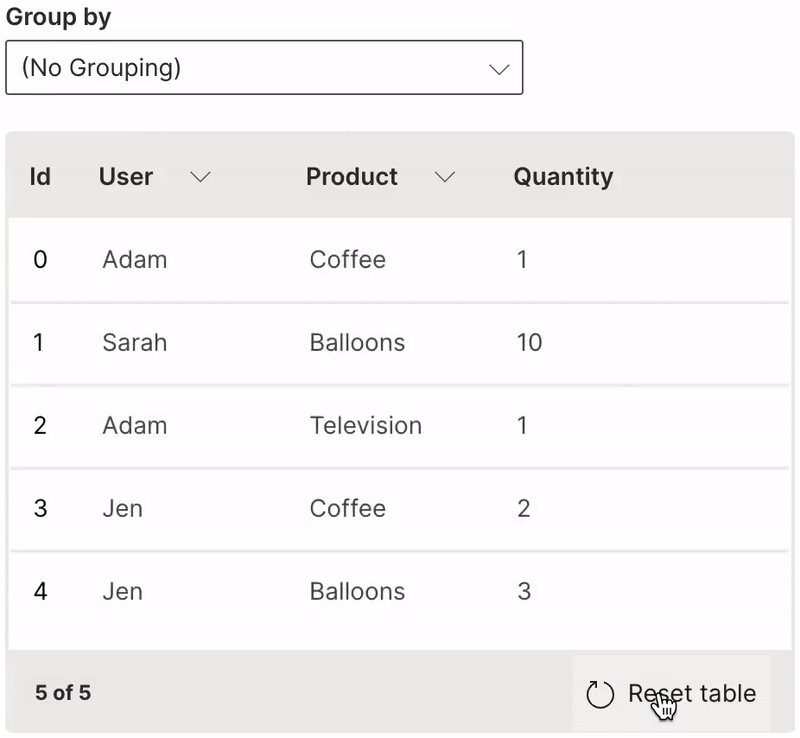

Wave Table (Group)
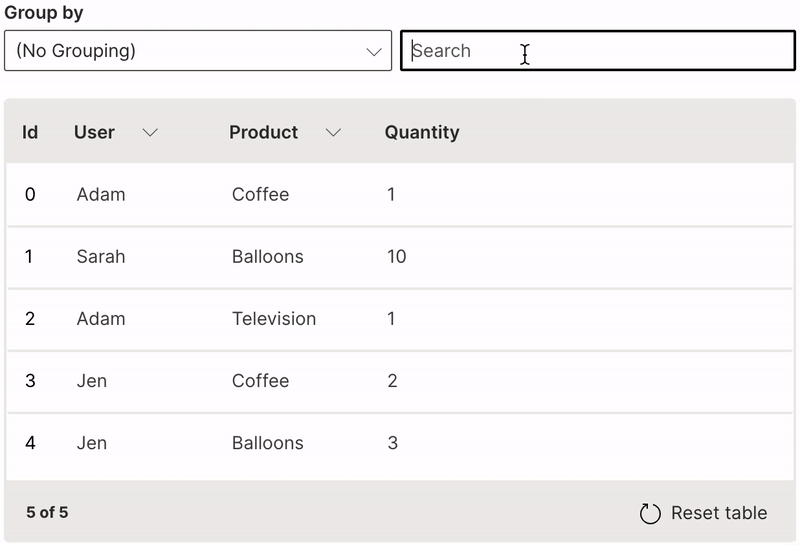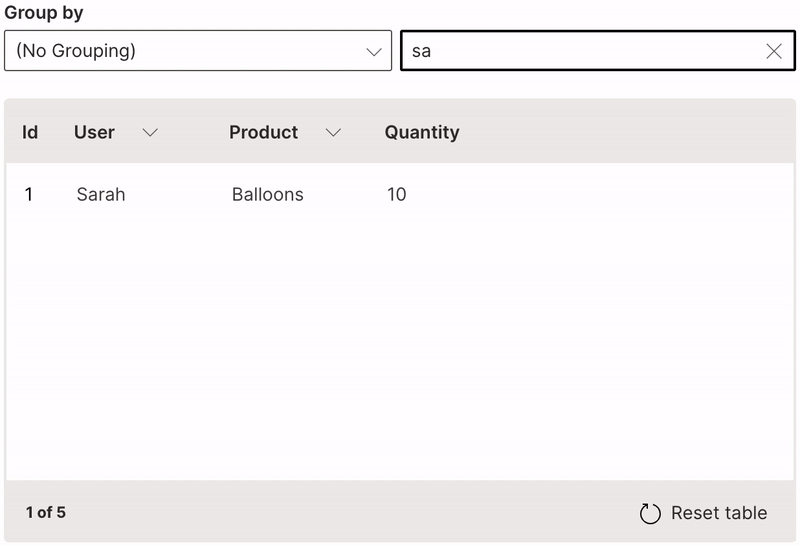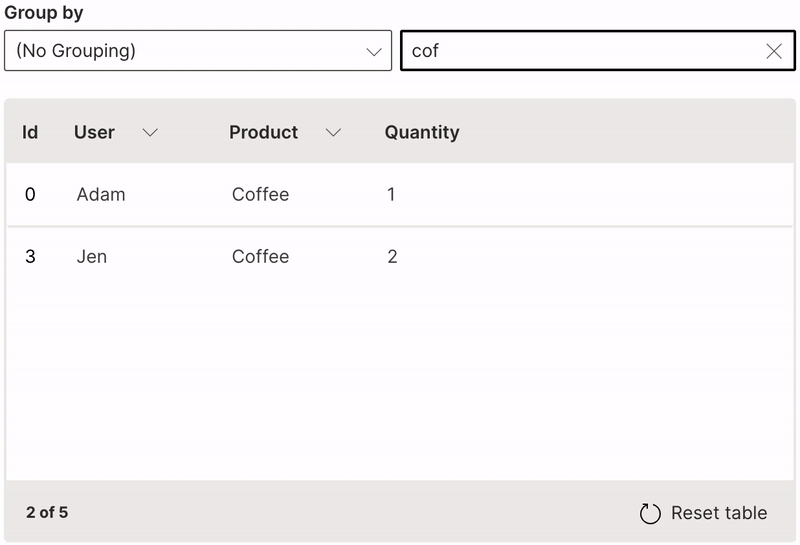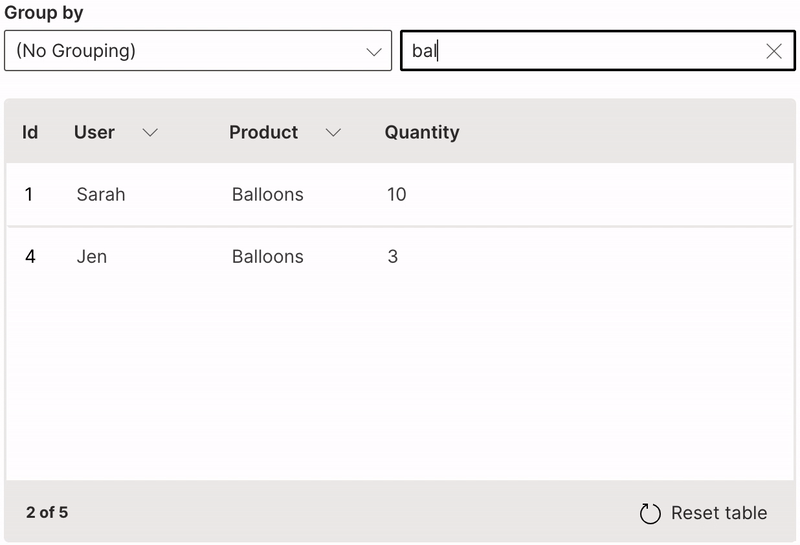
Search
A table can be filtered based on full or partial keyword search.
searchable is used to enable searching on a column. When text is entered in the search field, every row is shown that contains a match in at least one of its searchable columns.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='user',
label='User',
searchable=True
),
ui.table_column(
name='product',
label='Product',
searchable=True
),
...
],
...
)

Wave Table (Search)
Icon
A column of icons can be added natively to a table.
cell_type is used to define the icon column with ui.icon_table_cell_type.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='icon',
label='Icon',
cell_type=ui.icon_table_cell_type(),
min_width='30px'
),
...
],
rows=[
ui.table_row(name='0', cells=[..., 'CoffeeScript', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='1', cells=[..., 'Balloons', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='2', cells=[..., 'TVMonitor', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='3', cells=[..., 'CoffeeScript', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='4', cells=[..., 'Balloons', ...])
],
...
)
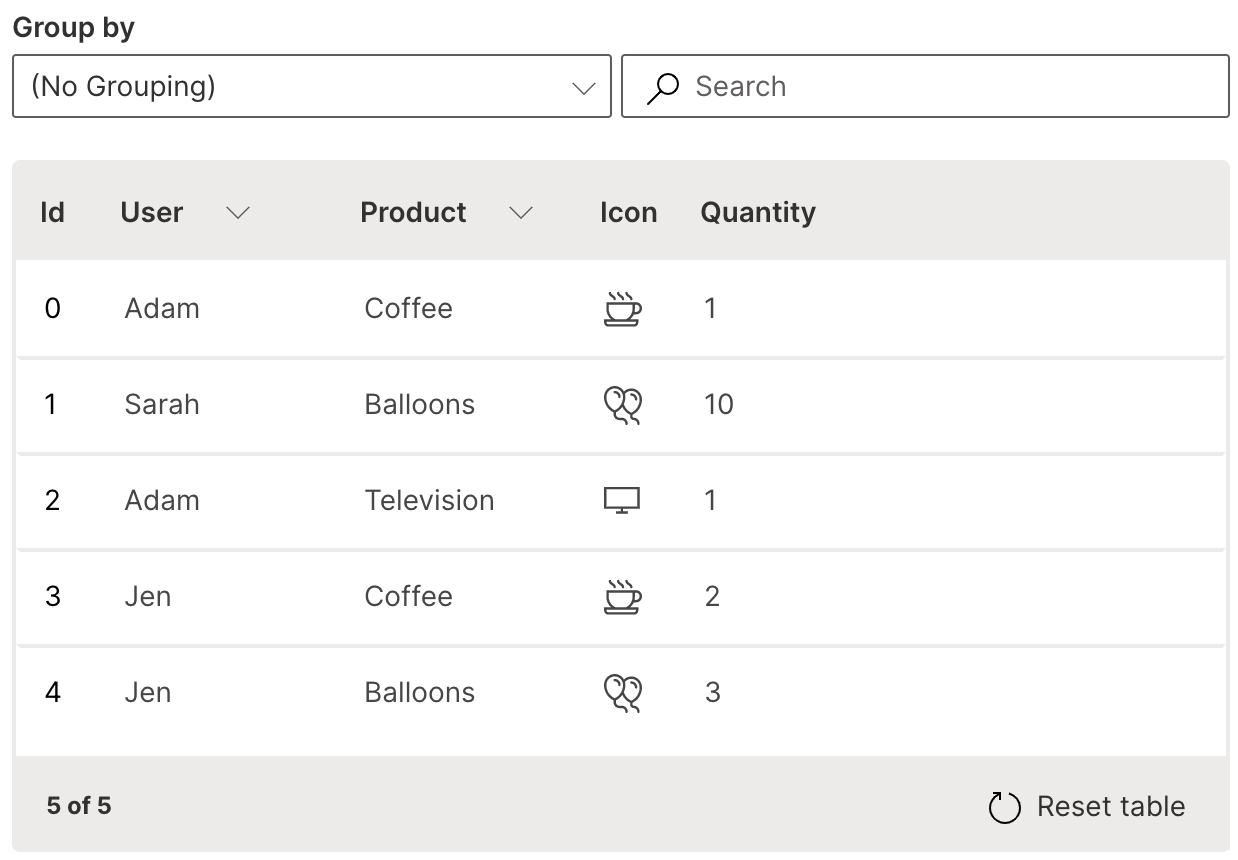

Wave Table (Icon)
The list of supported icons is available here.
Percentage
A column of percentages can be added natively to a table in the form of a circular progress icon.
cell_type is used to define the percentage column with ui.progress_table_cell_type.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='discount',
label='Discount',
cell_type=ui.progress_table_cell_type(),
sortable=True,
min_width='80px'
)
],
rows=[
ui.table_row(name='0', cells=[..., '0.09']),
ui.table_row(name='1', cells=[..., '0.66']),
ui.table_row(name='2', cells=[..., '0']),
ui.table_row(name='3', cells=[..., '0']),
ui.table_row(name='4', cells=[..., '0.15'])
],
...
)
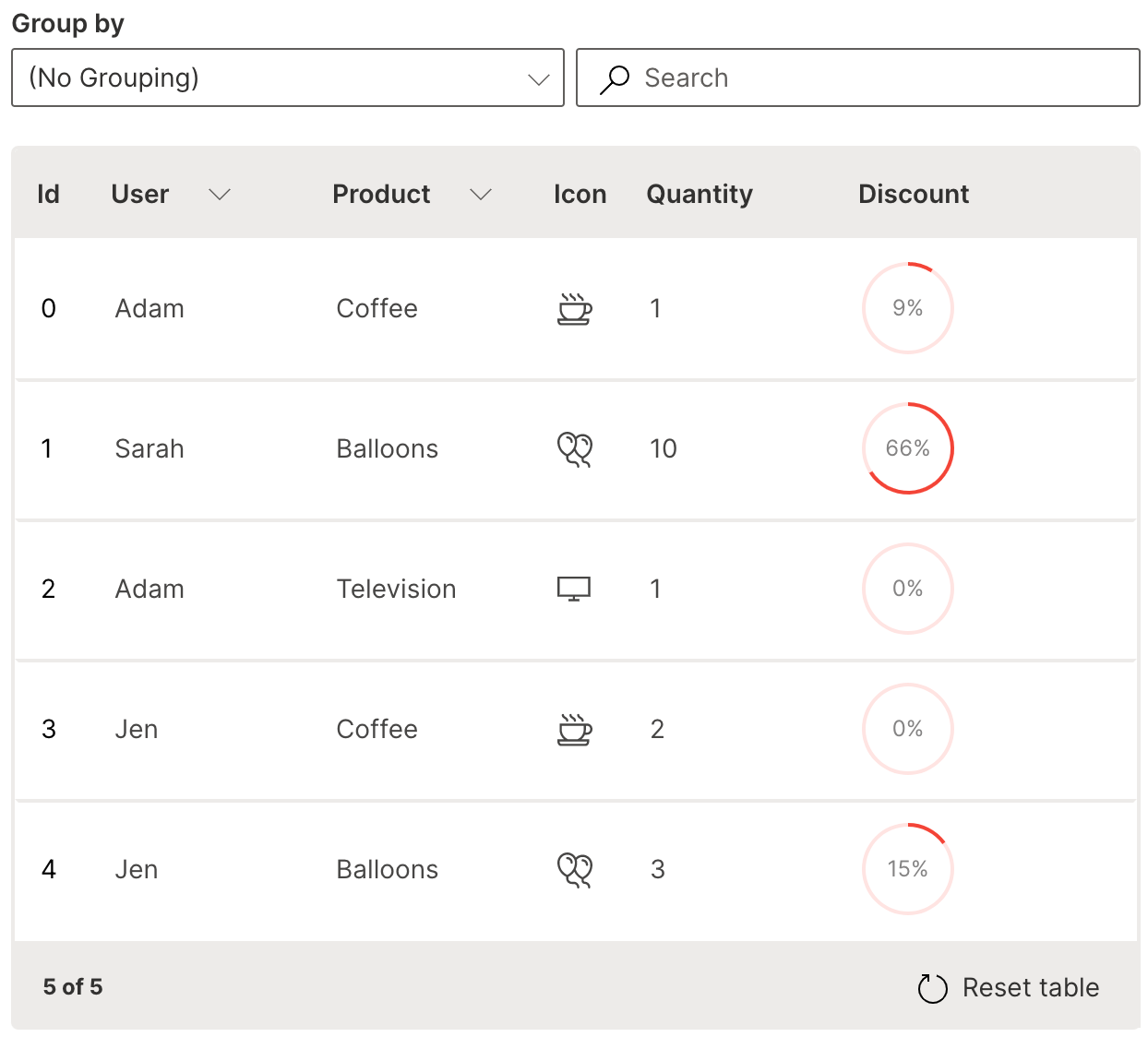

Wave Table (Percentage)
Tag
A column of single or multiple tags can be added natively to a table.
cell_type is used to define the tag column with ui.tag_table_cell_type to define the list of tags.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='tags',
label='Tags,
cell_type=ui.tag_table_cell_type(
name='',
tags=[
ui.tag(label='Beverage', color='$brown'),
ui.tag(label='Home', color='$blue'),
ui.tag(label='Retail', color='$green'),
ui.tag(label='Sale', color='$red')
]
)
)
],
rows=[
ui.table_row(name='0', cells=[..., 'Beverage,Sale']),
ui.table_row(name='1', cells=[..., 'Home,Sale']),
ui.table_row(name='2', cells=[..., 'Retail']),
ui.table_row(name='3', cells=[..., 'Beverage']),
ui.table_row(name='4', cells=[..., 'Home,Sale'])
],
...
)
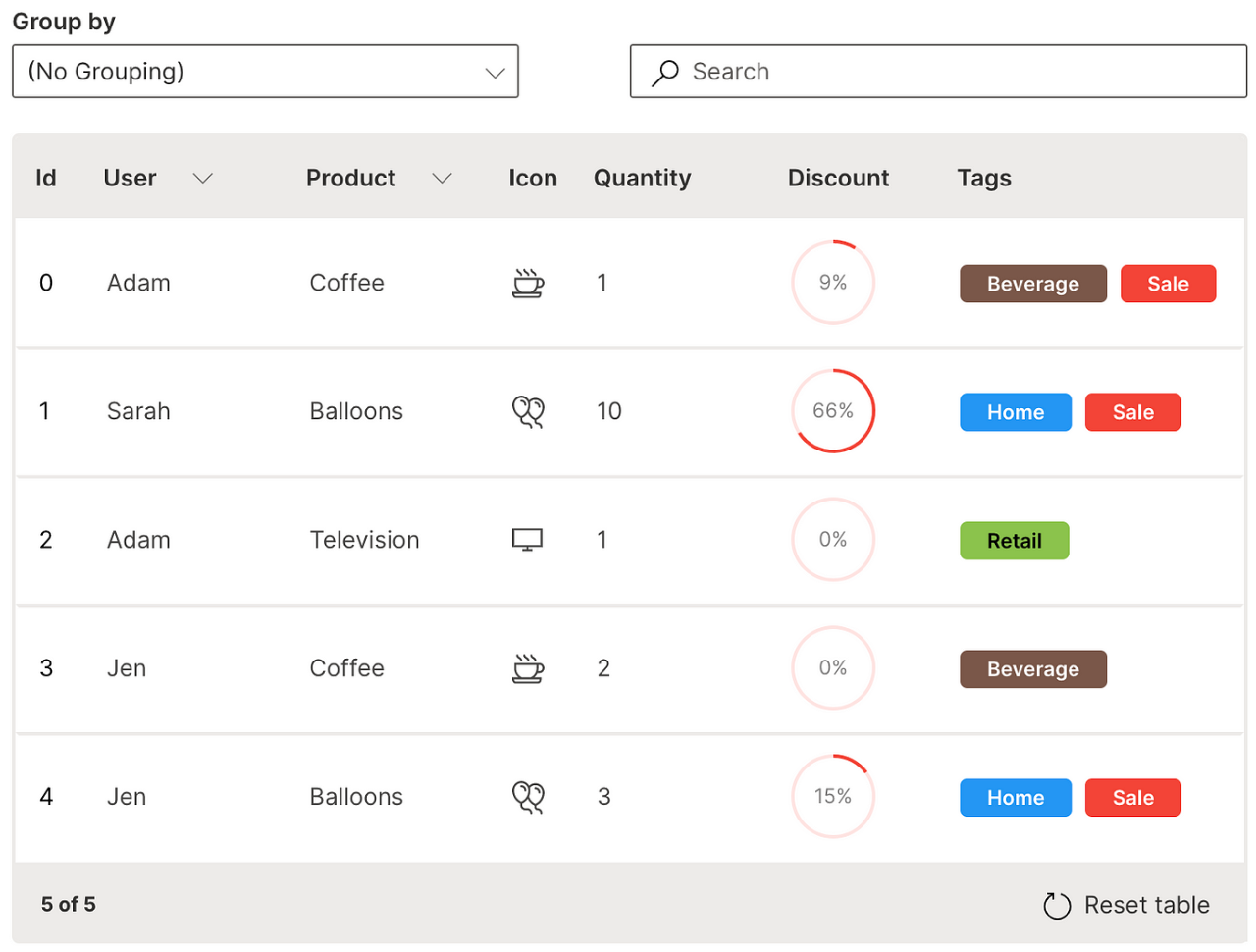

Wave Table (Tag)
Markdown
A column can be formatted as markdown text in a table.
cell_type is used to define the markdown column with ui.markdown_table_cell_type.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='description',
label='Description',
cell_type=ui.markdown_table_cell_type(),
searchable=True
),
...
],
rows=[
ui.table_row(name='0', cells=[..., '**Product**: *Coffee*\n**Category**: *Beverages*', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='1', cells=[..., '**Product**: *Balloons*\n**Category**: *Home*', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='2', cells=[..., '**Product**: *Television*\n**Category**: *Retail*', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='3', cells=[..., '**Product**: *Coffee*\n**Category**: *Beverages*', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='4', cells=[..., '**Product**: *Balloons*\n**Category**: *Home*', ...])
],
...
)
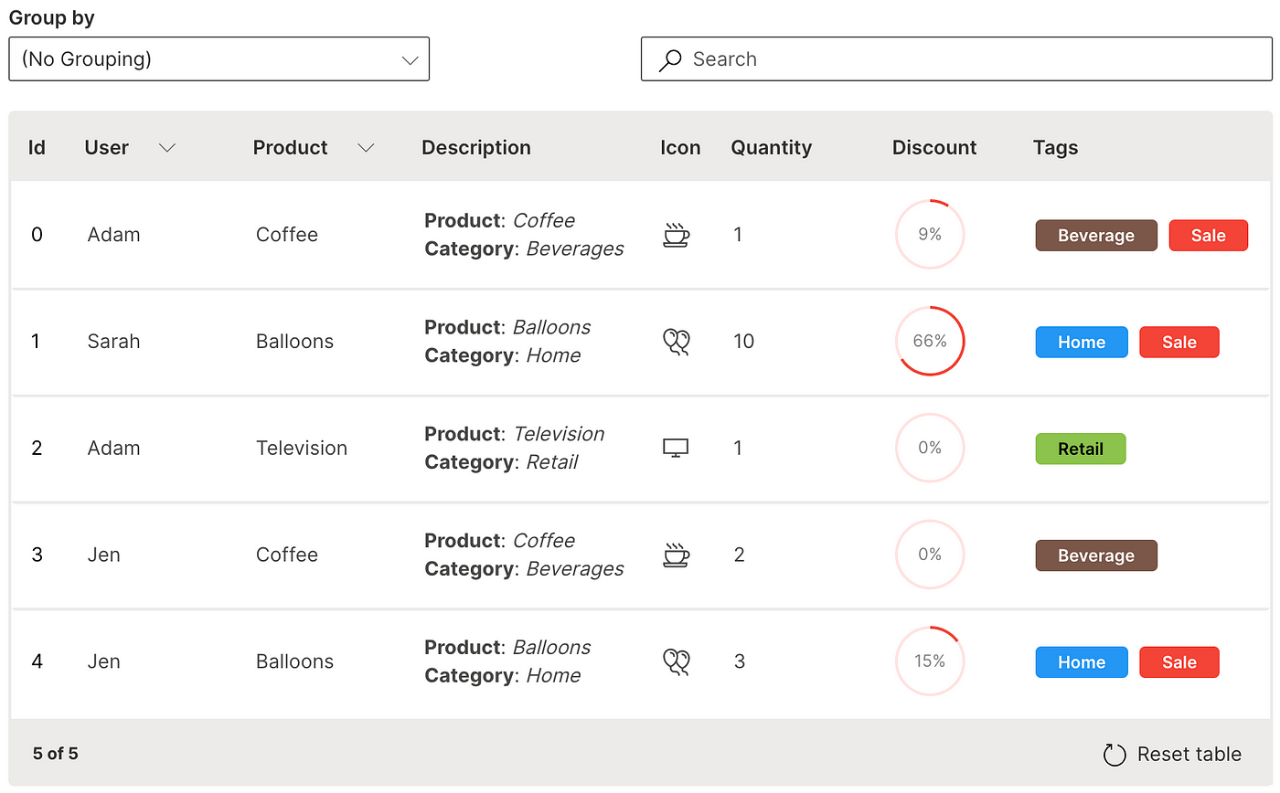

Wave Table (Markdown)
Image
The markdown formatting can be extended into an image column in a table.
cell_type is used to define the image column with ui.markdown_table_cell_type.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='picture',
label='Picture',
cell_type=ui.markdown_table_cell_type(),
searchable=True
),
...
],
rows=[
ui.table_row(name='0', cells=[..., '<center><img src="https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1587049016823-69ef9d68bd44" width="70%">', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='1', cells=[..., '<center><img src="https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1574276254982-d209f79d673a" width="70%">', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='2', cells=[..., '<center><img src="https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1552975084-6e027cd345c2" width="70%">', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='3', cells=[..., '<center><img src="https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1587049016823-69ef9d68bd44" width="70%">', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='4', cells=[..., '<center><img src="https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1574276254982-d209f79d673a" width="70%">', ...])
],
...
)
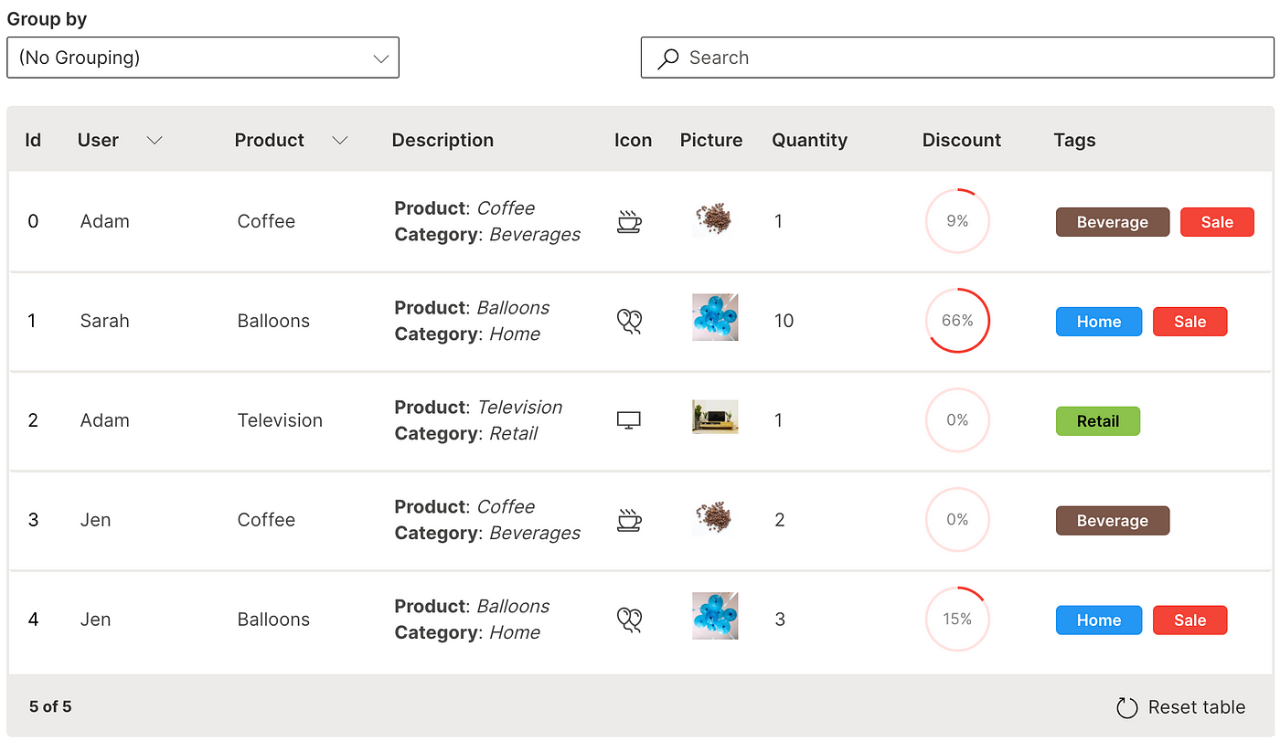

Wave Table (Image)
Audio
The markdown formatting can be extended into an audio column in a table where the embedded audio file can be played.
cell_type is used to define the image column with ui.markdown_table_cell_type.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='audio',
label='Audio',
cell_type=ui.markdown_table_cell_type(),
searchable=True
),
...
],
rows=[
ui.table_row(name='0', cells=[..., '<center><audio controls><source src="https://media.merriam-webster.com/audio/prons/en/us/mp3/c/coffee01.mp3" type="audio/wav">', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='1', cells=[..., '<center><audio controls><source src="https://media.merriam-webster.com/audio/prons/en/us/mp3/b/balloo01.mp3" type="audio/wav">', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='2', cells=[..., '<center><audio controls><source src="https://media.merriam-webster.com/audio/prons/en/us/mp3/t/televi03.mp3" type="audio/wav">', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='3', cells=[..., '<center><audio controls><source src="https://media.merriam-webster.com/audio/prons/en/us/mp3/c/coffee01.mp3" type="audio/wav">', ...]),
ui.table_row(name='4', cells=[..., '<center><audio controls><source src="https://media.merriam-webster.com/audio/prons/en/us/mp3/b/balloo01.mp3" type="audio/wav">', ...])
],
...
)
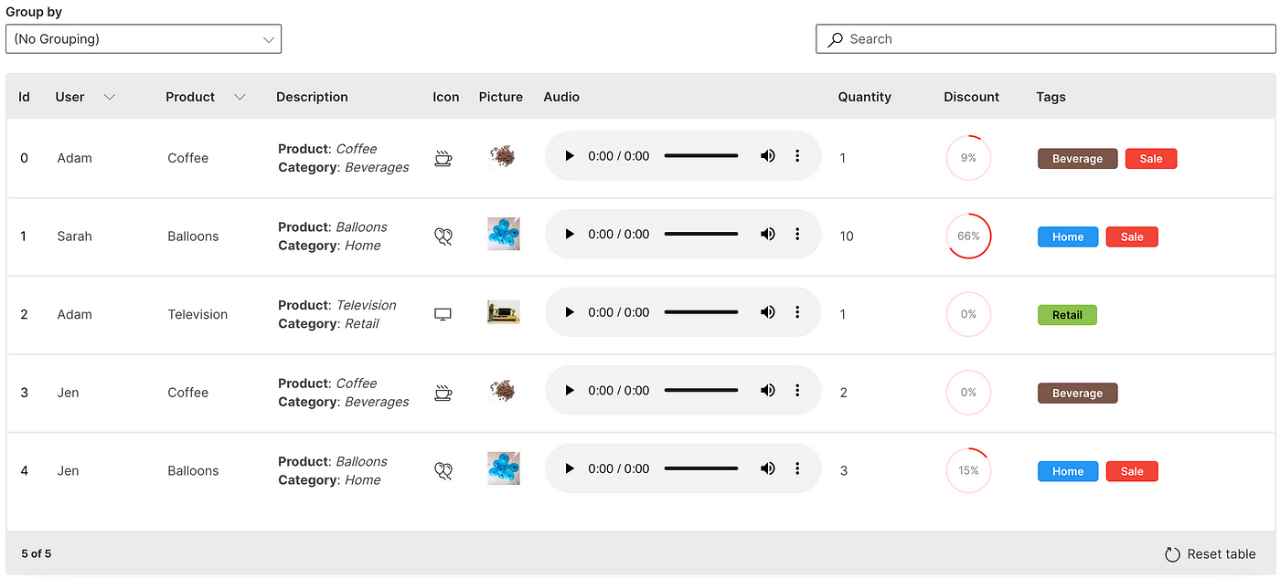

Wave Table (Audio)
Menu
Multiple custom actions can be performed on a row of a table.
ui.menu is used to provide the list of actions.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...,
ui.table_column(
name='menu',
label='Menu',
cell_type=ui.menu_table_cell_type(
commands=[
ui.command(name='view_transaction', label='View Transaction', icon='Shop'),
ui.command(name='view_image', label='View Image', icon='ImageSearch')
]
)
)
],
...
)
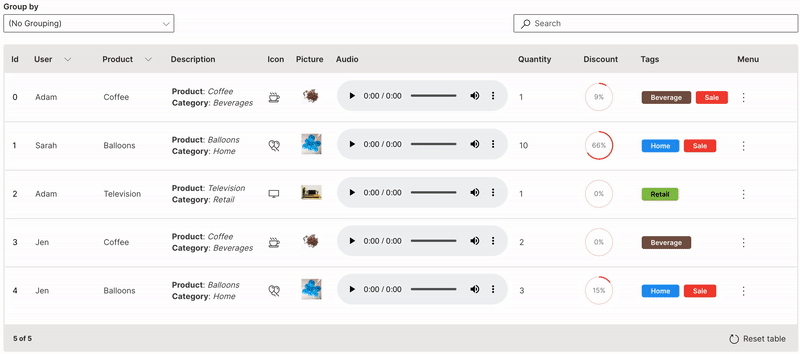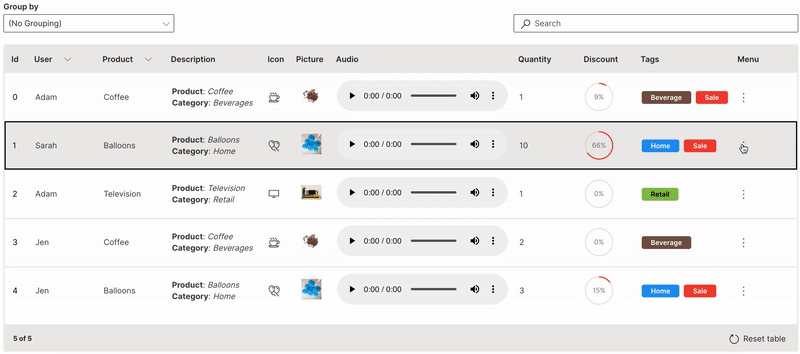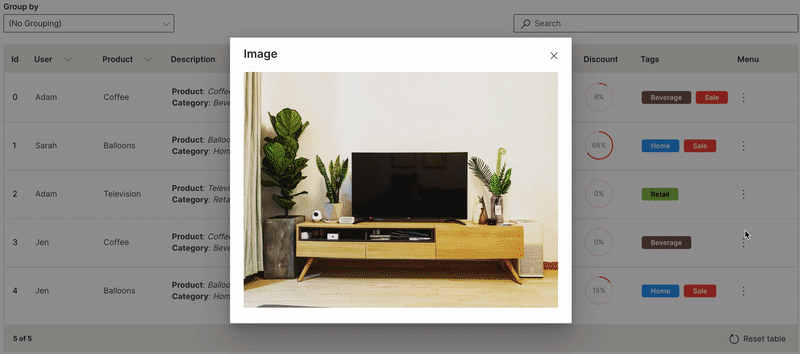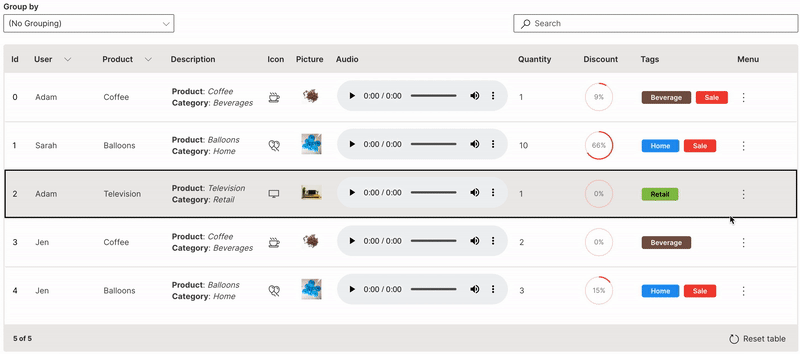

Wave Table (Menu)
Trigger
A row trigger can be set to perform a single action on a row of a table.
link is used to define the trigger column. Only one column (typically the id or key column) can be enabled for the trigger to be clicked on. Double-clicking anywhere on a row also triggers the same for that row.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
ui.table_column(
name='id',
label='Id',
link=True
),
...
],
...
)
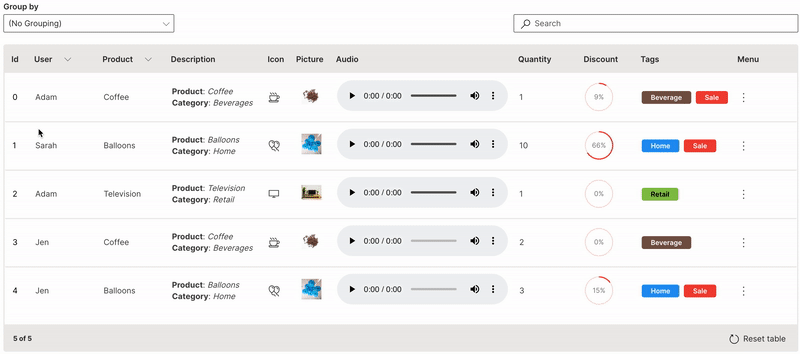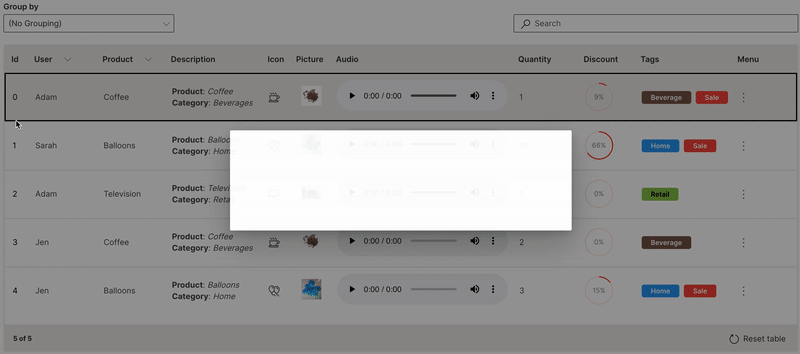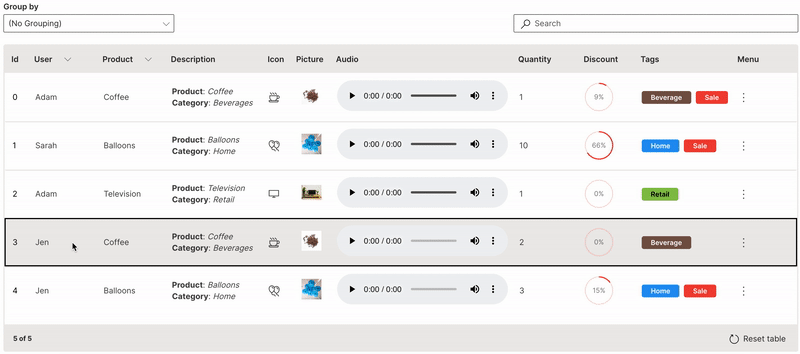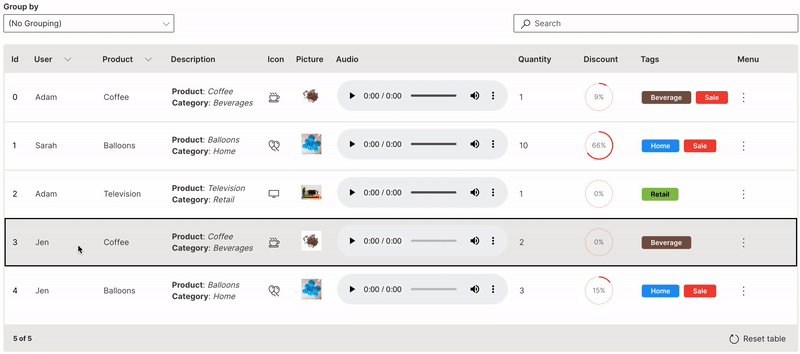

Wave Table (Trigger)
Multiselect
Actions can be performed on multiple rows together in a table.
multiple is used to enable multi-selection of rows in a table.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...
],
multiple=True,
...
)
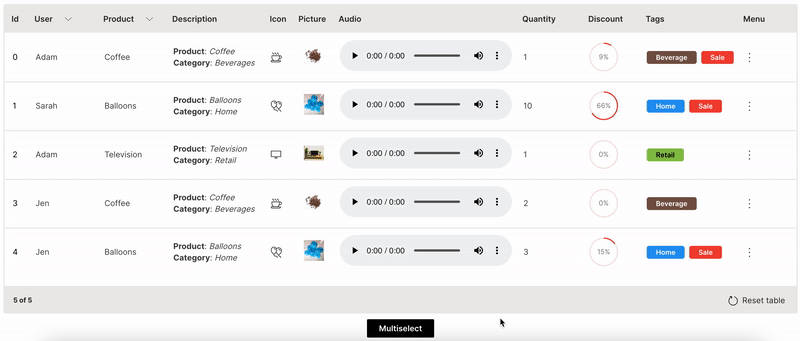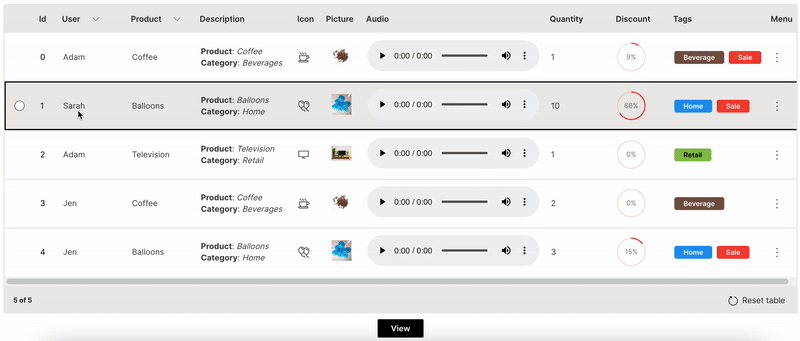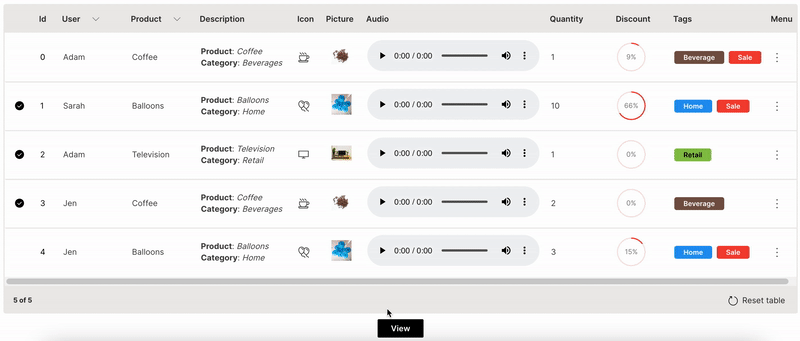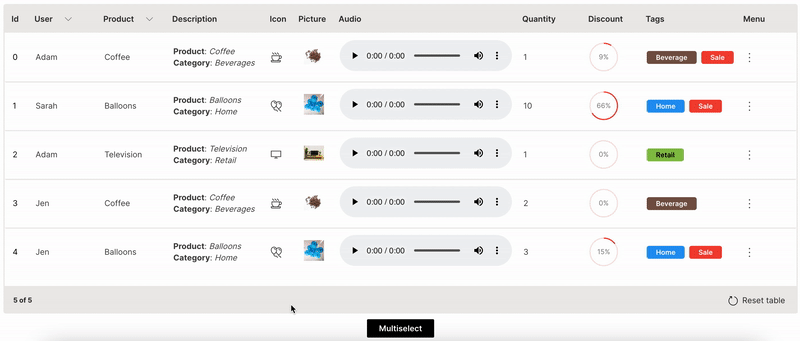

Wave Table (Multiselect)
Paginate
Large datasets can be handled effectively by paginating the table.
pagination is used to define the number of rows to paginate. rows needs to be filtered based on the page_change event.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...
],
rows=[
...
],
pagination=ui.table_pagination(total_rows=5, rows_per_page=2),
events=['page_change']
...
)
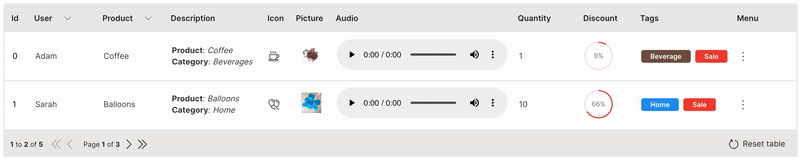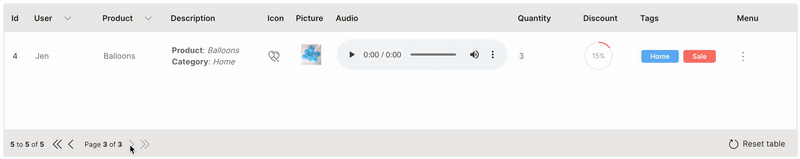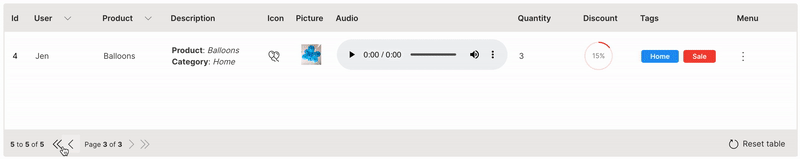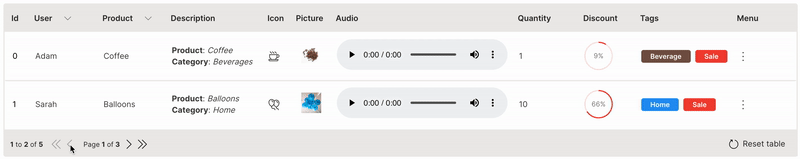

Wave Table (Paginate)
Download
A table can be downloaded in csv format.
downloadable is used to enable downloading of a table.
ui.table(
name='table_name',
columns=[
...
],
downloadable=True,
...
)
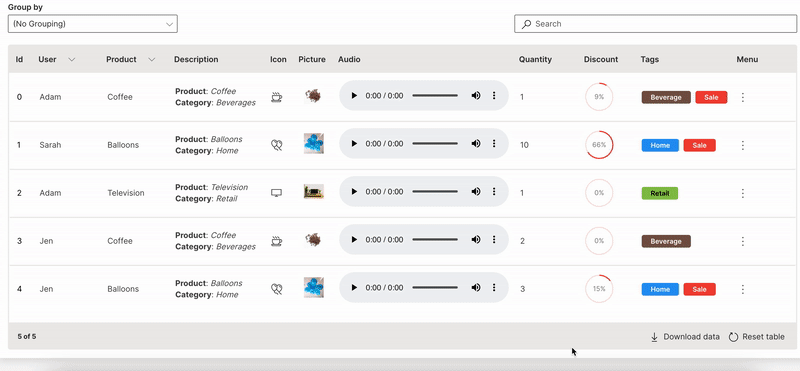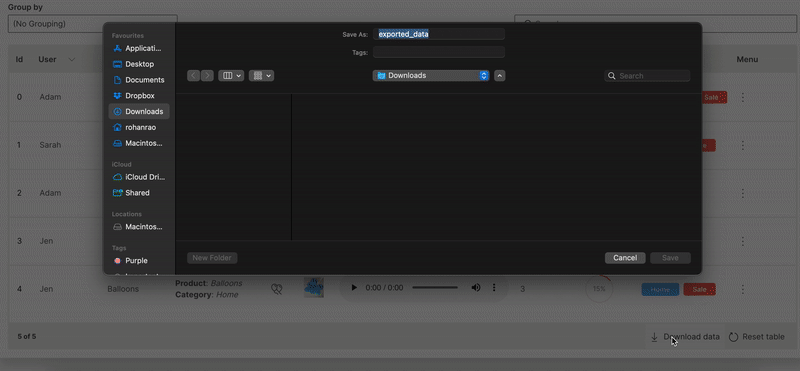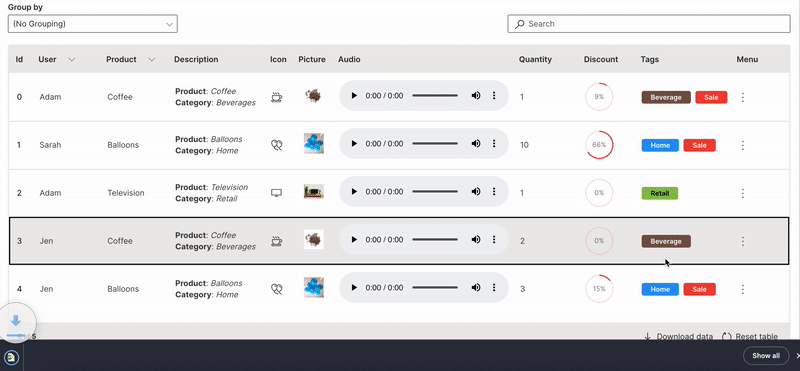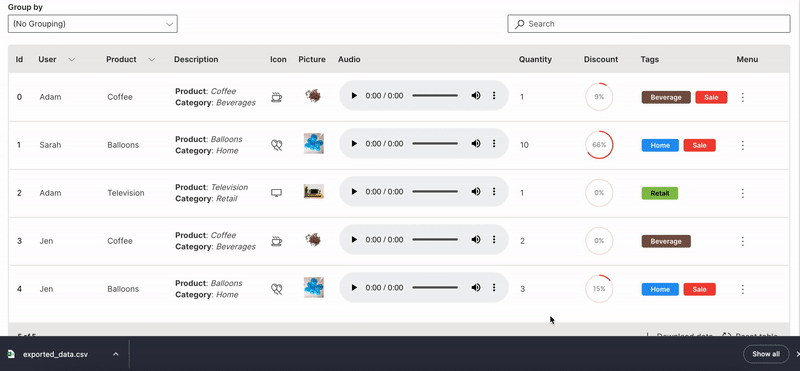

Wave Table (Download)
You can do a lot with H2O Wave’s Table component! It empowers data scientists and analysts to build stuff being more productive and efficient.
These snippets of code help to get started on extending it for different datasets and use cases.
Table Showcase
A full blown comprehensive application Table Showcase is also available as part of the WaveTon series that also provides accompanying code to handle the interactions and is recommended as a starting point to customize a table.
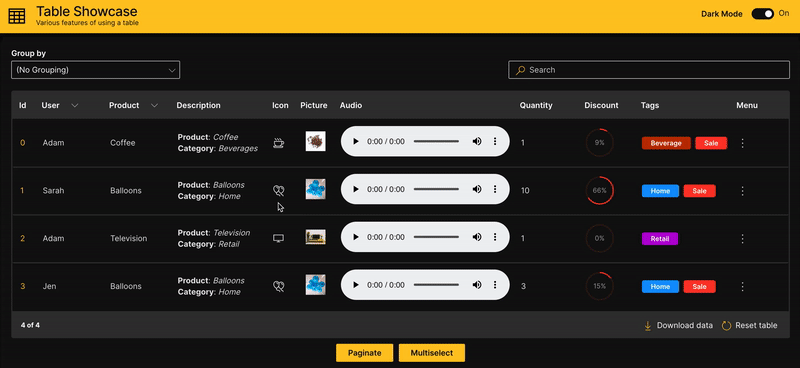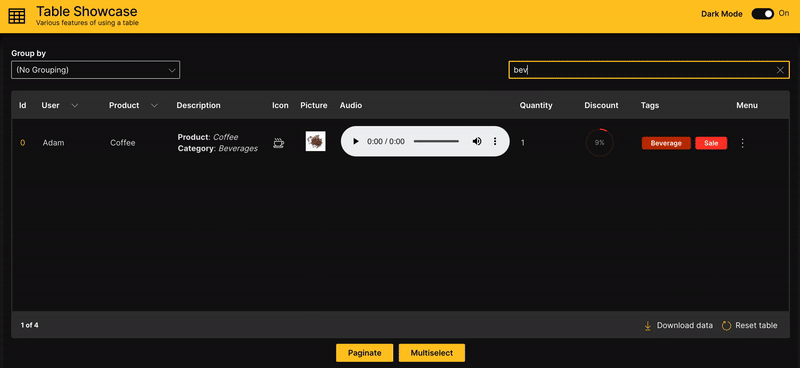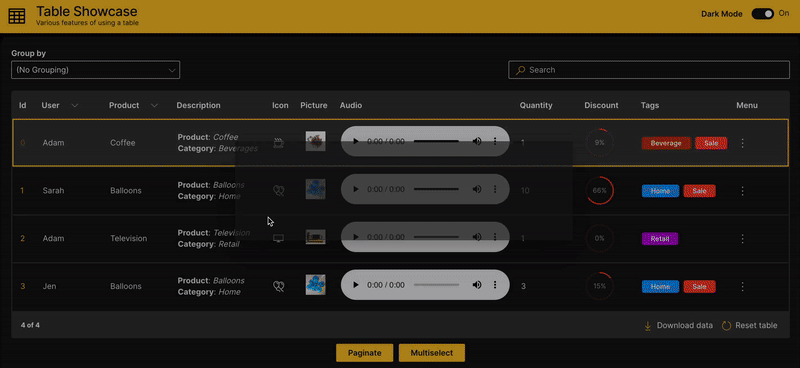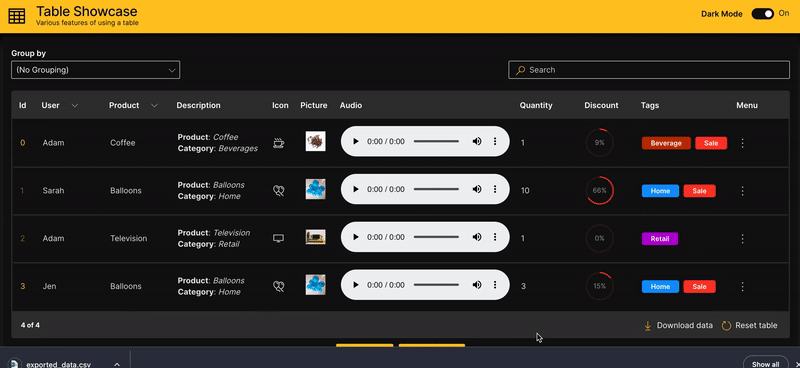

Table Showcase
Resources & References