Introducing H2O Hydrogen Torch: A No-code Deep Learning Framework


Over and over again we heard from customers, “deep learning is cool, but it’s hard and time consuming.” They kept asking “could someone just make it easier?”
In typical “Maker” fashion, you ask, we deliver, H2O Hydrogen Torch .
H2O Hydrogen Torch is a new product that enables data scientists and developers to train and deploy state-of-the-art deep learning models without writing a line of code. With H2O Hydrogen Torch, we’re continuing to democratize AI, by democratizing deep learning.


While H2O Hydrogen Torch makes it much easier and faster to build great deep learning models, we didn’t forget about the expert controls for our experienced data scientists. H2O Hydrogen Torch provides insights and full access to parameter tuning, so experts have control to dial in their models.
PyTorch is Awesome, So Let’s Make It Simple
As the name suggests, H2O Hydrogen Torch , leverages the outstanding engineering of the PyTorch library and builds upon it with pre-built training routines and optimized parameters for common deep learning use cases. H2O.ai’s set of Kaggle Grandmasters, the top data scientists in the world, developed these routines, making it simple to build state-of-the-art models.
Okay let’s dig in.
Model Training
H2O Hydrogen Torch takes care of training deep learning models for you. It’s seriously as easy as 1-2-3.
- Load your data.
- Select the problem type and set the hyperparameters (defaults already provided).
- Click train.
Yeah, that’s really it.
As mentioned earlier, H2O Hydrogen Torch is built to support different levels of data science experience. Novice users can build their first deep learning model quickly following best practices from our Kaggle Grandmasters without the struggle of getting through a steep learning curve, while expert users have all options to push model performance to the next level.
Users of H2O Hydrogen Torch will have the ability to learn about deep learning at their own pace, while creating models at the same time. After getting familiar with the basic training routine, novice users can enable a more experienced mode that will allow them to use more advanced settings and train more accurate models. The experts can start with the most advanced mode that displays all available settings, covering all the important state-of-the-art aspects of a deep learning model training.
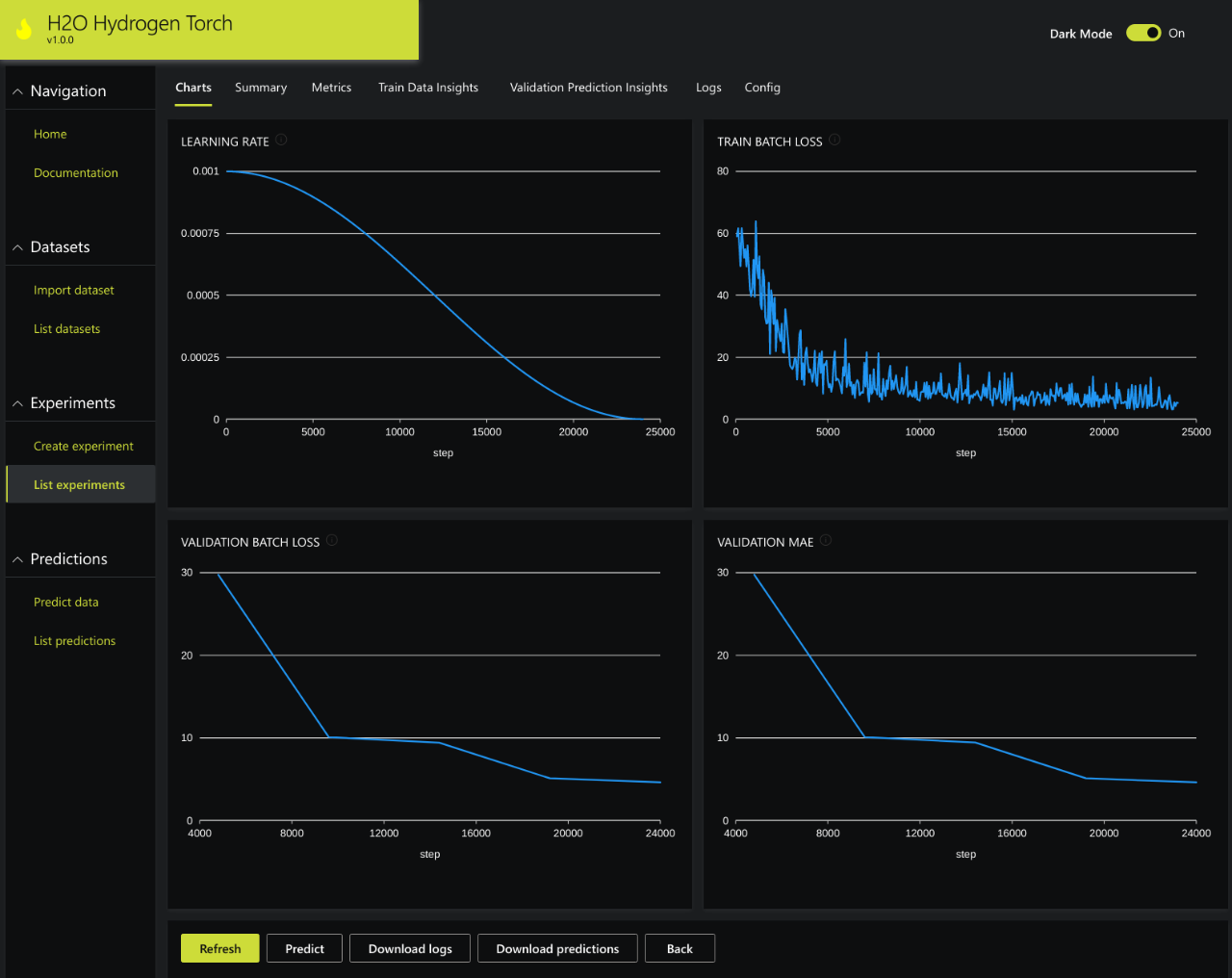

The model training is designed with scalability in mind. It supports multi-GPU training, allowing to allocate as many GPUs per task as needed.
Insights
We want data scientists to be confident in the models they are creating, therefore, both quantitative and qualitative model insights are an integral part of our product. We provide data scientists with a detailed overview of the model training process to identify any signs of unexpected behavior. A data scientist can evaluate the model accuracy with multiple metrics and assess model robustness by applying different decision thresholds. We provide visualizations of model predictions for a better understanding of how the model works and to help identify examples the model finds more challenging.
Model Deployment
Being a part of H2O AI Cloud , H2O Hydrogen Torch natively supports model deployment within the platform. That makes it extremely easy to bring your deep learning models into production. The neural network architecture and weights, as well as all the required dependencies, are automatically packaged and can be transferred to H2O MLOps , the tool to serve and monitor machine learning models. In case you are using an alternative way to run your models, that’s not a problem – the model package can also be deployed to an external environment by utilizing a scoring pipeline that can be downloaded for a finalized model. We also offer batch prediction functionality directly in the application, where also different inference settings can be compared.
Problem Types
H2O Hydrogen Torch is a flexible, but powerful backend, capable of solving a large variety of deep learning problems powered by state-of-the-art transfer learning . Currently, computer vision and natural language processing are in focus, being the most common tasks for deep learning and most common data assets in companies. We are continuously committed to expanding the scope of supported problems for the product, driven by direct customer needs and use cases. In detail, we currently support the following problem types.
Computer Vision
In computer vision, H2O Hydrogen Torch enables practitioners to train state-of-the-art models for the following problem types.
Image Classification/Regression
This classical computer vision use case is applied when the goal is to classify or predict a continuous target given an image as input. Possible applications include: for classification (i) predicting the type of landscape from drone photos, or for regression (ii) count the sum of coins from photos . We also support both multi-class and multi-label classification, and also for regression multiple simultaneous targets can be predicted.
Image Object Detection
The goal is to detect objects in images and to draw bounding boxes around all of them. Additionally, boxes can stem from different classes. Possible applications include: (i) detecting whether chest X-rays contain pneumonia and drawing a bounding box around the area of the disease, (ii) detecting vehicles in traffic or drone cameras, or (iii) detecting required pieces during an assembly process.
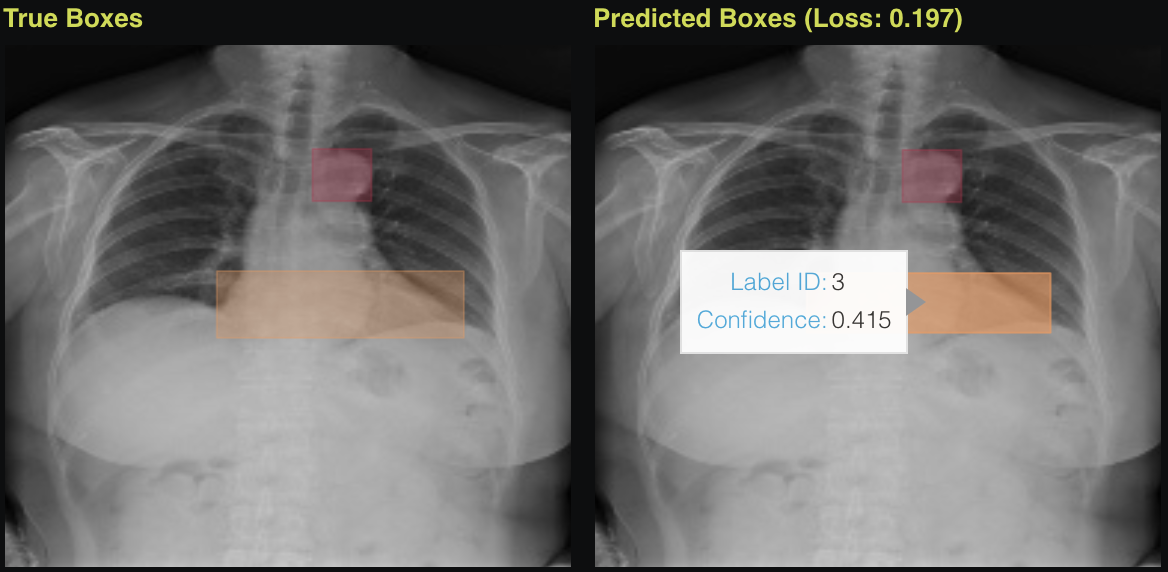

Image Semantic Segmentation
The task is to cluster parts of an image together that belong to the same object class. So instead of drawing bounding boxes as in object detection, we directly predict each pixel of an image and assign it to a separate class. Applications include: (i) segmenting road areas from videos captured using a dashcam, (ii) locating exact forms of objects of interest in medical images, or (iii) cutting out objects from the background.
Image Instance Segmentation
The task is to locate individual objects in images by drawing masks around all of them. So unlike semantic segmentation, each class in the image can have multiple instances that we need to separate. Applications include: (i) segmenting individual cars, pedestrians, or other objects from videos captured using a dashcam, (ii) detecting and delineating distinct objects of interest in biological images.


Image Metric Learning
In metric learning, we are not directly predicting a class or label of an image, but we attempt to create embedding (vector ) representations with the property that similar images exhibit similar embeddings. After creating embeddings, one can apply a similarity metric on the embeddings, such as cosine similarity, in order to identify these similar embeddings. Usually, metric learning models are trained on large sets of original classes, where each class contains only a few examples. Possible applications are specifically located in the area of recommender systems and for example contain: (i) searching and recommending identical products in an e-commerce store, or (ii) finding similar images, such as similar landmarks in a database.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
In natural language processing, H2O Hydrogen Torch currently enables practitioners to train state-of-the-art models for the following problem types. For all listed problem types, we utilize a wide range of state-of-the-art language models for transfer learning, allowing us to support multilingual & domain-specific language support.
Text Classification/Regression
Similar to image classification and regression, we aim at predicting a class or regression target given text as input. Possible applications include: (i) predicting customer satisfaction from transcribed phone calls, or (ii) categorizing incoming emails from customers and forwarding them to appropriate departments.
Text Token Classification
In-text token classification, we do not aim at classifying full-text passages, but rather locate and classify individual tokens or entities in text. Typical use cases include: (i) extracting entities such as drugs, or diseases from medical texts, or (ii) applying named entity extraction.


Text Span Classification
The goal is to identify relevant subsets of texts given a query. This task often is also referred to as question answering, as one attempts to query documents and ask questions about their content. Typical use cases include: (i) finding relevant information from medical transcripts, or (ii) building a company-specific question-answering system.


Text Sequence to Sequence
The task is to transform an input text sequence into a new output text sequence. The output text does not necessarily need to contain text passages from the input text. Typical use cases include: (i) translating from one language to another, (ii) simplifying text containing domain-specific terms, or (iii) automatically summarizing texts for better content understanding.
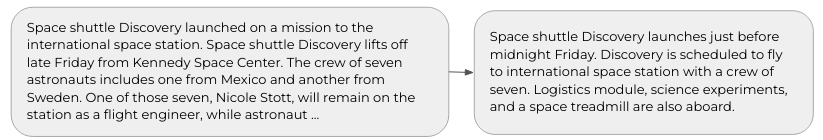

Text Metric Learning
Similar to image metric learning, the goal is to predict embedding (vector) representations of text input so that similar texts exhibit similar vector representations in embedding space. With a similarity metric such as cosine similarity, similar texts can be identified. Possible applications include: (i) detecting fake reviews which are similar to each other, (ii) finding similar questions in a user forum, or (iii) recommending articles based on similar descriptions.
How to Get Started
Experimenting with H2O Hydrogen Torch is simple, as it’s available in the H2O AI Cloud. Request a demo here . Once you’re in the service, fire up our simple tutorial to start making with the product.